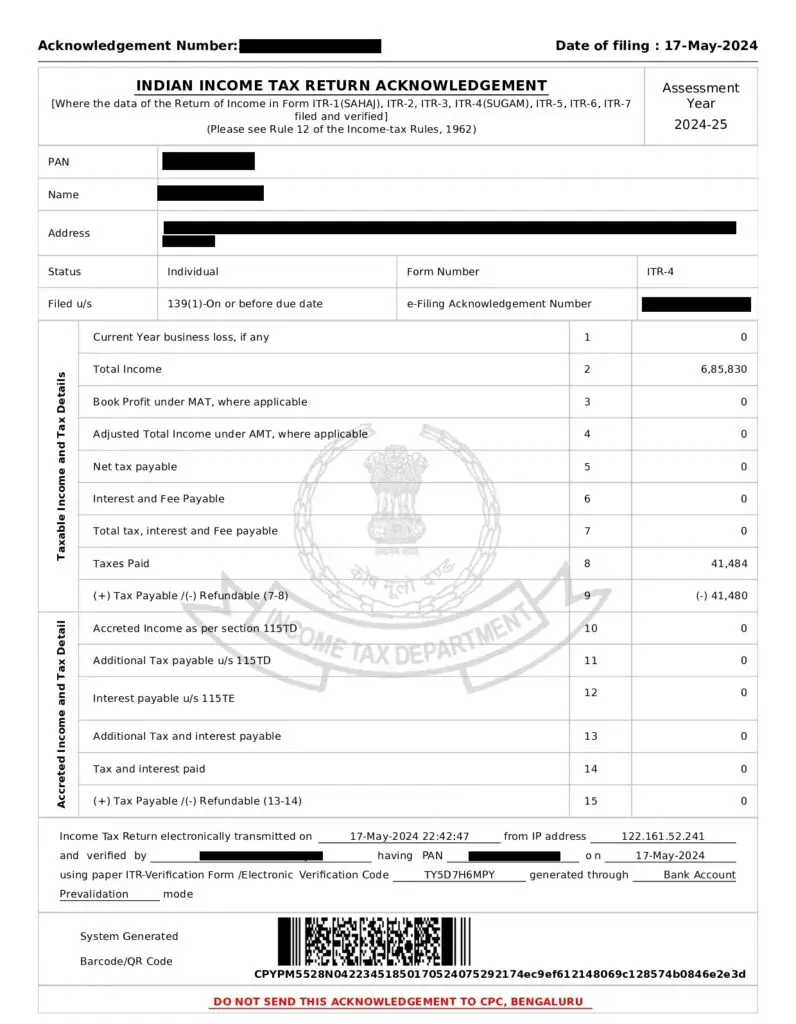
Income Tax Return Filing for AY 2024-25
Income Tax Return Filing for AY 2024-25 has been started. The last date to file Income Tax Return (ITR) for FY 2023-24 (AY 2024-25) without a late fee is 31st July 2024. File Your ITR within due date in order to avoid penalty and to avail tax saving investment benefits under old tax regime. Order Now.
Pricing Summary
for AY 2024-25
₹
999/-
-
Computation
-
ITR acknowledgment
-
Filed ITR form
Order Now
Cover Income from Salary, Rental and Business only